
E-Invoicing and Its Geopolitical Stakes
France’s electronic invoicing reform relies on a Y-architecture, where Partner Dematerialization Providers (PDPs) play a central role in issuing and…
Generix Announces the Appointment of Olivier Vaillancourt as General Manager for North America View the press release

A Warehouse Management System (WMS) is a software application designed to optimize the daily operations of a warehouse. It helps manage and control various processes, such as inventory management, picking, packing, shipping, and receiving, ensuring that everything runs smoothly and efficiently. By integrating a WMS into your operations, you can gain greater visibility and control over your inventory, leading to improved accuracy and reduced costs.
A WMS typically includes several critical components that work together to streamline warehouse operations:
For a deeper understanding of the intricate workings of a WMS system, stay tuned for our upcoming in-depth article on this topic.
Understanding how a WMS system works is essential for leveraging its full potential. A WMS integrates with your existing systems, such as ERP and order management software, to provide real-time visibility into your inventory and warehouse operations.
For a deeper understanding of the intricate workings of a WMS system, stay tuned for our upcoming in-depth article on this topic.
Understanding the different types of Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) is crucial to choosing the right solution for your business. Various WMS systems are designed to meet specific operational needs and scales. Here are the main types:
Choosing the right type of WMS depends on your specific business needs. For a more detailed exploration of WMS types, you can refer to our in-depth article on navigating through types of Warehouse Management Systems.

A WMS system does much more than just track inventory. It plays a crucial role in enhancing the efficiency of your warehouse operations by automating and optimizing various processes. Below are the key functionalities of a WMS:
One of the primary functions of a WMS is to provide real-time visibility into your inventory levels. This visibility allows you to maintain accurate stock levels, reduce instances of overstocking or stockouts, and ensure that you always have the right products available when needed.
A WMS helps streamline the order fulfillment process by automating picking, packing, and shipping tasks. By optimizing these processes, a WMS reduces the time it takes to fulfill orders, improves order accuracy, and enhances customer satisfaction.
Effective space utilization is critical in a warehouse. A WMS helps you optimize your warehouse layout by suggesting the most efficient storage locations for your products based on product velocity and size. This optimization leads to faster picking times and better use of available space.
A WMS also plays a vital role in managing warehouse labor. It assigns tasks to workers based on their skills and availability, tracks their performance, and identifies areas where productivity can be improved. A WMS helps reduce operational costs and increase efficiency by optimizing labor resources.
A WMS can automate the replenishment process to prevent stockouts and ensure that popular items are always available. The system monitors inventory levels in real-time, and triggers reorder when stock falls below a predefined threshold. This automation minimizes the risk of lost sales due to out-of-stock items.
In industries where compliance and traceability are critical, a WMS ensures that your warehouse operations meet regulatory requirements. The system can track the movement of goods throughout the supply chain, providing detailed records of each product’s journey from supplier to customer.
A robust WMS offers a wide range of features that enhance warehouse operations. Below are some of the most important features you should look for in a WMS:
A WMS provides real-time inventory tracking, allowing you to monitor stock levels, product locations, and movement within the warehouse. This feature is essential for maintaining accurate inventory records and preventing discrepancies.
Efficient order processing is a critical feature of any WMS. The system should automate the picking, packing, and shipping processes, ensuring that orders are fulfilled quickly and accurately. Advanced WMS solutions also offer multi-channel order management, allowing you to manage orders from various sales channels in a single system.
A WMS should offer comprehensive reporting and analytics capabilities. These tools provide valuable insights into your warehouse operations, helping you identify trends, monitor key performance indicators (KPIs), and make decisions to improve efficiency.
Modern WMS solutions offer mobile access, allowing warehouse staff to use handheld devices for inventory counting, picking, and receiving tasks. Mobile integration enhances the flexibility and accuracy of warehouse operations.
A WMS should include automated alerts and notifications that inform you of critical events, such as low inventory levels or delayed shipments. These alerts help you respond quickly to potential issues and maintain smooth operations.
The benefits of implementing a WMS are numerous, making it a valuable investment for any warehouse operation. Here are some of the key advantages:
A WMS significantly increases efficiency and productivity by automating and optimizing warehouse processes. Tasks that were once manual and time-consuming, such as inventory counting and order picking, can be completed faster and more accurately.
A WMS helps reduce costs in several ways. Improving inventory accuracy reduces the need for safety stock, minimizing storage costs. The system also optimizes labor resources, reducing overtime and improving overall productivity.
With faster order fulfillment and improved accuracy, a WMS contributes to higher customer satisfaction. Customers receive their orders on time and in perfect condition, increasing loyalty and repeat business.
A WMS is scalable, meaning it can grow with your business. Whether expanding your warehouse operations or adding new sales channels, a WMS can adapt to your changing needs, ensuring that your warehouse remains efficient and effective.
The advanced reporting and analytics capabilities of a WMS provide you with the data you need to make informed decisions. Whether you’re considering changes to your warehouse layout or evaluating the performance of your staff, a WMS gives you the insights you need to make the right choices.
When considering a WMS system, it’s important to understand the differences between SaaS WMS and cloud-based WMS. While both are hosted in the cloud, they offer distinct benefits and drawbacks that may influence your decision.
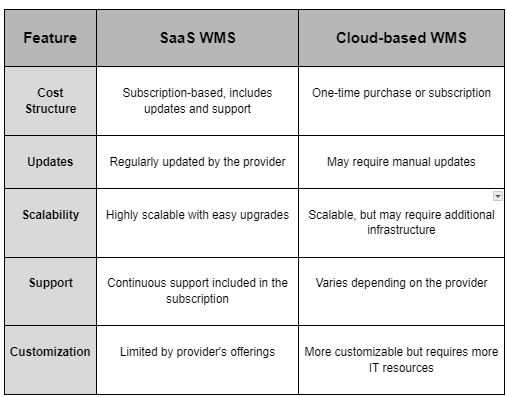
Like those offered by Generix, SaaS WMS systems provide a flexible, cost-effective solution with regular updates and strong support, making them ideal for businesses looking to stay ahead in a competitive market. For more information on the benefits of SaaS WMS, explore our article on the benefits of switching to a SaaS warehouse management system.
When selecting a WMS, it’s important to consider your specific needs and requirements. Not all WMS solutions are created equal, and the right system for your business will depend on factors such as the size of your warehouse, the complexity of your operations, and your budget.
Start by assessing your warehouse needs. Consider factors such as the volume of inventory you manage, the number of orders you process daily, and the complexity of your warehouse layout. This assessment will help you determine your desired features and capabilities in a WMS.
Ensure your WMS is compatible with your existing systems, such as your ERP or order management software. Integration is key to ensuring seamless operations and avoiding data silos.
Implementing a WMS is a significant investment, so choosing a vendor that offers strong support and training is important. Look for vendors that provide comprehensive onboarding and ongoing support to ensure your team can use the system effectively.
Choose a WMS that can scale with your business. As your warehouse operations grow, you want a system that can handle increased inventory, more orders, and additional locations. Future-proofing your WMS will save you time and money in the long run.
Finally, consider the cost of the WMS, including implementation, training, and ongoing maintenance. While it’s important to stay within your budget, remember that a WMS is an investment in the efficiency and success of your warehouse operations.
A Warehouse Management System (WMS) is an essential tool for optimizing warehouse operations, improving efficiency, and reducing costs. A WMS enhances inventory accuracy, speeds up order fulfillment, and boosts customer satisfaction by automating and streamlining key processes. When choosing a WMS, it’s important to assess your warehouse needs, consider integration and compatibility, evaluate vendor support, and ensure scalability. With the right WMS in place, your warehouse can achieve new levels of productivity and efficiency, positioning your business for long-term success. For those seeking a cutting-edge solution, consider the Generix Solochain WMS as your partner in optimizing warehouse management.

France’s electronic invoicing reform relies on a Y-architecture, where Partner Dematerialization Providers (PDPs) play a central role in issuing and…

The B2B mandate in Germany, set to take effect on January 1, 2025, marks a crucial step in the European…

Following the October 15 announcement regarding the abandonment of the PPF development, the DGFIP and its partner AIFE are ramping…

Work with our team to build your ideal supply chain software stack and tailor it to your unique business needs.